M&A Outlook for 2025 and Beyond
- Published
- Feb 20, 2025
- Topics
- Share
The M&A markets, as with other commercial and financial sectors globally, were profoundly affected by the COVID-19 pandemic and its subsequent repercussions. U.S. market transaction values averaged about $3.57 trillion between 2015 and 2019. This figure dropped to $2.71 trillion in 2020 but rebounded to $4.76 trillion in 2021 and $3.39 trillion in 2022. This fluctuation was due to canceling numerous transactions in 2020, which re-entered the market in 2021 and 2022. Conversely, the value of bankruptcies and restructurings peaked at $28.9 billion in 2020 before significantly declining in 2021 and 2022. During the same period, European markets were additionally affected by the war in Ukraine, and the shock to the energy markets was caused by economic sanctions imposed on Russia. 2023 was a down year in M&A activity, but 2024 has rebounded to pre-COVID levels.
|
2015 |
2016 |
2017 |
2018 |
2019 |
2020 |
2021 |
2022 |
2023 |
2024 |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
M&A (PE & Corporate) |
$3.10Tn |
$3.23Tn |
$3.11Tn |
$3.15Tn |
$2.78Tn |
$2.02Tn |
$3.69Tn |
$2.86Tn |
$2.36Tn |
$3.16Tn |
|
Public Markets (Incl. IPOs) |
$355.99B |
$237.58B |
$294.02B |
$459.01B |
$242.66B |
$430.24B |
$618.17B |
$260.96B |
$235.03B |
$362.76B |
|
Venture Capital |
$148.94B |
$129.41B |
$139.30B |
$195.10B |
$203.92B |
$229.28B |
$455.15B |
$256.25B |
$169.38B |
$201.20B |
|
Bankruptcy and Restructuring |
$9.58B |
$18.95B |
$28.51B |
$5.94B |
$11.87B |
$29.82B |
$1.75B |
$11.86B |
$23.86B |
$12.11B |
|
Total |
$3.62Tn |
$3.61Tn |
$3.57Tn |
$3.81Tn |
$3.24Tn |
$2.71Tn |
$4.76Tn |
$3.39Tn |
$2.78Tn |
$3.73Tn |
Source: Pitchbook
The market movements become clearer when examining transaction values, and deal counts quarterly over the past twenty quarters. The correction started in the last quarter of 2020, peaked in the third quarter of 2021, and has remained flat or declined since then.
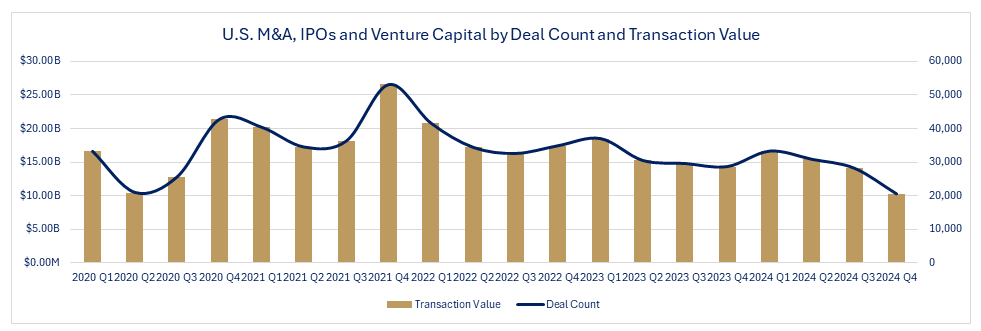
So, what is the outlook for M&A markets in 2025 and beyond? Factors that determine transaction value and deal counts include the availability of capital, interest rates and debt liquidity, economic conditions and market sentiment, advances in technology, regulatory environments, and geopolitical events.
Availability of Capital – Public Equity Markets
Capital for M&A activity is sourced from both public and private markets. Public market funding primarily comes from initial public offerings (IPOs), but secondary offerings, special purpose acquisition companies (SPACs), and private investments in public equities (PIPEs) are alternative sources. Over the past three years, U.S. IPO activity has been relatively low, peaking at $303 billion in value for 2021 before dropping to $56 billion in 2022, $30 billion in 2023, and $53 billion in 2024. Most of this decline can be explained by market volatility, poor post-IPO returns, and high interest rates, which yield high returns in fixed-income markets and are more attractive. However, we anticipate that lower interest rates, expected regulatory easing under the new government, and renewed interest in mid-cap companies will strengthen public markets in 2025 and beyond. Additionally, rising valuations of venture capital-owned companies are likely to increase the supply side of IPO candidates as VCs seek to exit their investments through IPOs and return capital to their investors.
Availability of Capital – Private Equity Markets
A significant demand-side driver of private or public company buyouts and divestitures is the substantial amount of capital raised but not yet invested by U.S. private equity funds. This capital, known as dry powder or the 'overhang,' currently exceeds $1 trillion in the U.S. and $1.6 trillion globally. General partners (GPs) who manage these funds do not receive their 20% profit margins until they exit an investment. This creates a causal link between their desire to earn more money and the pressure to generate returns by investing their limited partners' (LPs) money and subsequently exiting those investments. Although U.S. fundraising activity in 2024 was only 5% lower in value than in 2023, with $856 billion raised, it was still 26% lower compared to 2021 and 2021. However, the aggregate value, regardless of the vintage of the funds, is driving the demand-side pressure. We expect this pressure to be a significant driver of M&A transaction volume and value in 2025 and beyond.
Corporate Firepower
Although PE-backed M&A activity has been a significant driver of transaction volume and value over the past ten years, there is some evidence that corporate-led M&A activity has been closing the gap over the last two years. As a percentage of U.S. M&A transactions (excluding IPOs and VC investments), PE-backed activity climbed from a 22% share of total value in 2015 to over 42% by the end of 2022 before decreasing to 30% and 31% in 2023 and 2024, respectively. Corporate buyers rely on both their operating cash and debt to purchase companies. If they are a public company, they can also offer their stock as a form of payment. Corporate buyers are generally more active when there is a strong belief in forthcoming economic growth. Although the U.S. economy has been robust and growing over the past 3 years, public sentiment has been contradictory. Even at the corporate level, the fear of a hard landing as the economy cools down has had a dampening effect. In addition, a more aggressive anti-trust Department of Justice (DOJ) and Federal Trade Commission (FTC) leadership has created fear of mega-merger failures. However, the biggest obstacle to making bold moves has been (until recently) the unpredictability of the presidential and congressional elections. Now that that is known, we expect the effect of looser regulations, lower taxes, and lower interest rates to boost corporate M&A activity in 2025 and beyond significantly.
The Cost of Debt
A significant factor in recent declines in M&A activity has been the cost of borrowing money for leveraged buyouts. Higher interest rates have increased the cost of debt, compelling buyers to seek either lower equity valuations or more assured exit outcomes that would yield the same levels of returns as they would have achieved with lower debt payments. It has also made the debt service calculation a more important factor in deciding the amount of leverage to be borrowed. There is a very strong historical inverse correlation between interest rates and M&A activity, so we expect decreasing interest rates to boost all categories of M&A activity in 2025 and beyond. However, if tariffs reverse the recent decreases in inflation, interest rates may remain flat or even rise again.
The Power of AI
Suppose there is one technology that keeps virtually every CEO (and CTO) up at night. In that case, it is the rapid development of artificial intelligence (AI) and its impact on business operations, commerce, and economic activity. Although consumer-facing generative AI such as ChatGPT and DeepSeek have grabbed the headlines, it is the use of AI and machine learning within the ecosystem of business operations that is both a threat and opportunity to virtually every type of business universally. So, not surprisingly, companies that have developed AI technology currently have the highest valuations of all industry sectors. Still, businesses that have been early adopters of AI technology as part of their operations will also be attractive targets for larger companies with greater inertia in how they develop technology. So, expect M&A deals driven by technology intellectual property (IP) and adoption in 2025 and beyond.
The Economy
The overall health of the economy significantly influences M&A activity. Economic stability and growth encourage businesses to pursue mergers and acquisitions as a means of achieving expansion and gaining competitive advantages. Although the economic outlook for the U.S. is broadly positive, the threat of tariffs and other disruptions to international trade poses a major headwind to both public and private equity and debt markets. These uncertainties have the potential to depress M&A activity.
Market Sentiment
The confidence of investors and companies in the market can drive M&A activity. Positive market sentiment can lead to increased deal-making, while negative sentiment can result in a slowdown. The threat of tariffs and other disruptions to international trade has created volatility in the markets, which has a dampening effect on M&A activity.
Geopolitical Events
Events such as wars, trade disputes, and economic sanctions can significantly impact M&A markets. For instance, the war in Ukraine and the resulting shock to energy markets caused by economic sanctions on Russia have affected European M&A activity. The ongoing geopolitical uncertainty, including the future of Ukraine and the Middle East, is likely to have a negative impact on M&A activity.
Conclusion
The outlook for M&A activity in 2025 and beyond is mixed. While the PE overhang, lower interest rates, and a more business-friendly U.S. government are expected to boost M&A activity, the same government has also introduced uncertainty in the economy and the geopolitical order. This uncertainty is detrimental to M&A activity. Therefore, we anticipate a flat to slightly elevated M&A outlook for 2025 and the near future.
Contact EisnerAmper’s team using the form below to discuss how we can support your M&A strategy in 2025.
What's on Your Mind?
Start a conversation with Paren












